Chili Pepper: Plant, Benefits, Varieties and Recipes
Share
CHILLI PEPPER: PLANT, BENEFITS, VARIETIES AND RECIPES
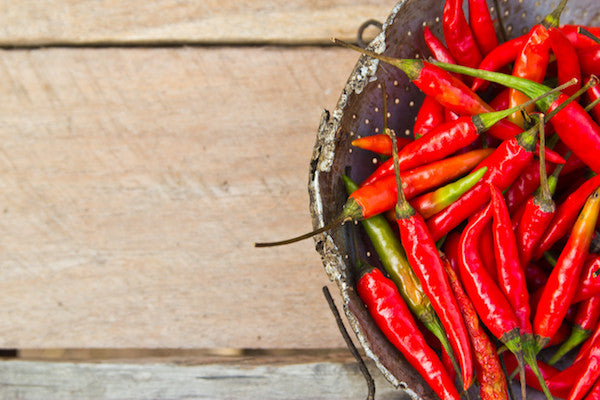
Chili pepper is the fruit of the plant of the same name belonging to the Solanaceae family. The Chili pepper plant (Capsicum) varies according to the species: there are plants more similar to shrubs and plants that instead reach two meters in height. This fruit has many properties and many benefits, but also a series of contraindications that should not be underestimated, so it is good to be careful not to abuse it in particular circumstances. But let's try to find out something more about hot and sweet chili peppers: here is everything you need to know about the plant, benefits and contraindications, the varieties (including the Calabrian chili pepper ), recipes and how to use fresh chili peppers .
CHILLI PEPPER: PLANT AND VARIETY
The chili pepper plant is native to America but today it is grown all over the world. In fact, we know that in 5500 BC it was grown in Mexico and used as a spice in Peru. It was Christopher Columbus who brought it to Europe in 1493, where it had enormous success. The chili pepper plant (Capsicum) changes according to the variety, going from small shrubs of 40-80 cm to plants of about 2 meters. The leaves are elliptical and ovate in shape and can reach 30 cm in length and 15 cm in width. The flowers are usually white, but some species have green or purple flowers. The fruits are berries with a wall that covers the pulp and an internal wall. Inside the fruit there is the placenta, very filamentous, which divides the berry into chambers. The seeds are smooth, and depending on the variety they can be light or dark. The fruits are distinguished according to their shape, size, color and degree of spiciness. There are 31 varieties of chili peppers, including both hot and sweet species. Of the 31 species, 5 are cultivated:
• Capsicum annuum: this is the most cultivated species in the world and includes both sweet pepper and hot pepper. Representative species include: common sweet pepper, Italian sweet pepper, cayenne pepper.
• Capsicum baccatum: the plant reaches up to 2 meters and produces many fruits, which can be small and rounded or lantern-shaped. The representative species are Aji pineapple, Heart drops, Bishop's hat.
• Capsicum chinense: these are the hottest peppers in the world, including Naga Jolokia, the hottest species in the world. Representative species: Tears of fire, habanero, Yellow Mushroom.
• Capsicum frutescens: it is a difficult species to grow in Italy, as the plant grows very slowly. Its fruits contain double the capsaicin (alkaloid that determines spiciness) compared to capsicum annuum. Representative species: Tabasco, Trifetti.
• Capsicum Pubescens: the plant is totally different from the others, as it is covered in hair, the flowers are purple and the seeds are black. Representative species: Rocoto de seda, Canario.
GROWING CHILI PEPPER
The chili pepper plant is very easy to grow, so you can have it at home and pick the fruits at the right time. Obviously, you need to evaluate the variety of chili pepper to grow, as some require very specific climatic conditions. The vast majority of Italians grow cayenne at home, a chili pepper that is easy to grow and offers a certain abundance of fruits. You can start growing the plant in spring, therefore between April and May (if you live in Calabria or in the South even towards the end of March). In the pots you need to put specific soil for horticultural plants and, once the seedlings are planted, they will need to be fertilized and watered very often. If looked after well, the plant will last for several years.
BENEFITS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS OF CHILI PEPPER
In addition to giving a more decisive flavor to dishes, chili pepper has various properties and benefits: in fact, it has therapeutic, slimming and some say aphrodisiac functions. Chili pepper is an excellent antioxidant and according to the latest scientific research it is very useful in preventing tumors. It also aids digestion, improves circulation and protects the cardiovascular system, since it is a good vasodilator. It has anti-inflammatory properties, in fact it is used to treat coughs, and is excellent for relieving rheumatic pain. It is rich in vitamin C and vitamin E, thanks to which it is said to be a powerful aphrodisiac. However, there are contraindications that should not be underestimated: chili pepper is not recommended for those suffering from ulcers, hemorrhoids, hepatitis, cystitis and gastroenteritis. Pregnant women and children under 12 cannot take it, as they have a very delicate digestive system.
HOT CHILI PEPPER: RECIPES
Here we are at the section we like the most: recipes with chili peppers! Let's say right away that we can use chili peppers to flavor our dishes: fresh or dried, it can add an extra touch, but obviously you have to ask your guests how delicate their palate is. There are many recipes with hot chili peppers: from the classic spaghetti with garlic, oil and chili peppers to chili and spicy sauces. Calabrian chili peppers are also used in preserves, together with vegetables or stuffed with tuna. They are also the basis of nduja and piccantino, a Calabrian sauce made with chili peppers, vegetables, anchovies and capers. Finally, chili peppers can also be used to prepare desserts: we can enjoy them with chocolate, use them in the preparation of cakes and ice creams and even make a good jam.
FRESH CHILI PEPPER: WHAT TO KNOW
Better fresh or dried chili pepper ? A nice dilemma, but we can say that it is delicious in both ways. However, chili pepper, consumed fresh, maintains more intact the nutritional properties that we have listed previously, and certainly has a stronger and more intense flavor. Dried and powdered chili pepper generally loses a bit of spiciness, but is still excellent to use in the preparation of specific dishes and when you have little time.
HOTTEST CHILI PEPPER: THE RANKING.
A little curiosity: every year a ranking of the hottest chili peppers in the world is drawn up according to the Scoville scale (SHU), created by the American chemist WL Scoville. In 2017, the Carolina Reaper (2,200,000 SHU) took first place, followed by: Trinidad Scorpion (1,463,700 SHU), Naga Viper (1,382,118 SHU), Bhut Jolokia (from 855,000 to 1,041,427 SHU) and Seven Pod Douglah (from 800,000 to 1,030,000 SHU).